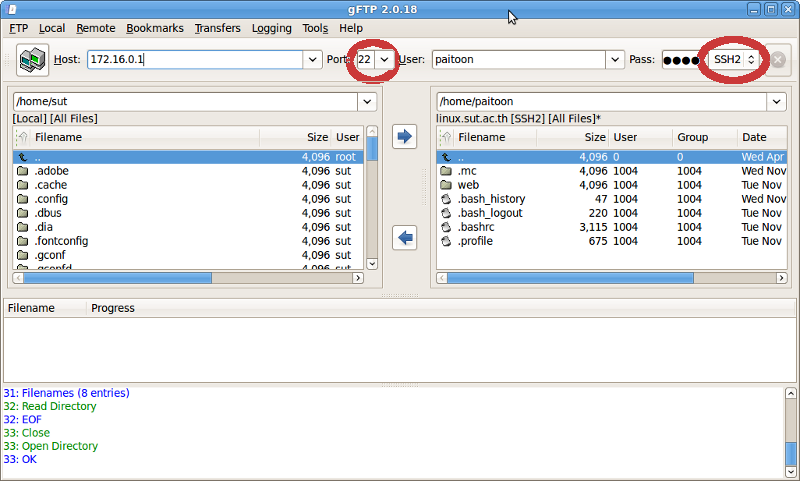
# Example config file /etc/vsftpd.conf
#
# The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file
# loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable.
# Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults.
#
# READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd
options.
# Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of
vsftpd's
# capabilities.
#
#
# Run standalone? vsftpd can run either from an inetd or as a
standalone
# daemon started from an initscript.
listen=YES
#
# Run standalone with IPv6?
# Like the listen parameter, except vsftpd will listen on an IPv6 socket
# instead of an IPv4 one. This parameter and the listen parameter are
mutually
# exclusive.
#listen_ipv6=YES
#
# Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this
out).
anonymous_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to allow local users to log in.
local_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command.
write_enable=YES
#
# Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to
022,
# if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's)
local_umask=022
#
# Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This
only
# has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also,
you will
# obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user.
#anon_upload_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create
# new directories.
#anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES
#
# Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they
# go into a certain directory.
dirmessage_enable=YES
#
# Activate logging of uploads/downloads.
xferlog_enable=YES
#
# Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data).
connect_from_port_20=YES
#
# If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned
by
# a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not
# recommended!
#chown_uploads=YES
#chown_username=whoever
#
# You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is
shown
# below.
#xferlog_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log
#
# If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog
format
#xferlog_std_format=YES
#
# You may change the default value for timing out an idle session.
#idle_session_timeout=600
#
# You may change the default value for timing out a data connection.
#data_connection_timeout=120
#
# It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which
the
# ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user.
#nopriv_user=ftpsecure
#
# Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests.
Not
# recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it,
# however, may confuse older FTP clients.
#async_abor_enable=YES
#
# By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact
ignore
# the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do
ASCII
# mangling on files when in ASCII mode.
# Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of
service
# attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd
# predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of
the
# raw file.
# ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol.
ascii_upload_enable=YES
ascii_download_enable=YES
#
# You may fully customise the login banner string:
ftpd_banner=Welcome to SUTinsServer FTP service.
#
# You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses.
Apparently
# useful for combatting certain DoS attacks.
#deny_email_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd.banned_emails
#
# You may restrict local users to their home directories. See the
FAQ for
# the possible risks in this before using chroot_local_user or
# chroot_list_enable below.
chroot_local_user=YES
#
# You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their
home
# directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list
of
# users to NOT chroot().
#chroot_list_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
#
# You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled
by
# default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on
large
# sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror"
assume
# the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for
enabling it.
#ls_recurse_enable=YES
#
#
# Debian customization
#
# Some of vsftpd's settings don't fit the Debian filesystem layout by
# default. These settings are more Debian-friendly.
#
# This option should be the name of a directory which is empty.
Also, the
# directory should not be writable by the ftp user. This directory is
used
# as a secure chroot() jail at times vsftpd does not require filesystem
# access.
secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd
#
# This string is the name of the PAM service vsftpd will use.
pam_service_name=vsftpd
#
# This option specifies the location of the RSA certificate to use for
SSL
# encrypted connections.
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# This option specifies the location of the RSA key to use for SSL
# encrypted connections.
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
|